Origami’s Smart Permissions
Origami’s Smart Permissions system allows for robust and dynamic access control based on user groups and user roles, providing fine-grained control over what different users can view, edit, or delete within the system. Here’s a breakdown of how the permissions work:
1. User Groups and Roles
- User Groups are defined in the system settings under User Management.
- Users can belong to multiple groups, and for each user, you can define whether they are an administrator of specific user groups or individuals within those groups.
- Inherited Permissions: If a user is defined as an administrator of a group, they inherit tOrigami’s Smart Permissions system allows for robust and dynamic access control based on user groups and user roles, providing fine-grained control over what different users can view, edit, or delete within the system. Here’s a breakdown of how the permissions work:
- the permissions of the users within that group.
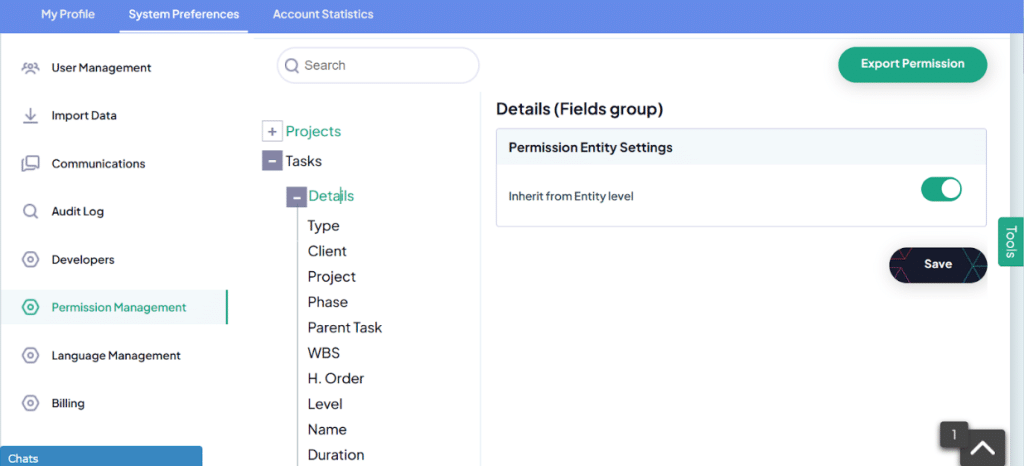
2. Permission Levels at the Entity Hierarchy
- The permission settings start at the entity level (highest in the hierarchy) and offer various access controls. The key permission levels are:
- Full Permission: Users can create, delete, view, and edit everything.
- View Only: Users can only view the data.
- Edit and View: Users can view and edit the data.
- Full Permission to Owner Instance: Users can create, delete, and edit only the records they have created.
3. Team Permissions
- There’s an additional checkbox for team permissions: when enabled, users can be granted view only or edit and view permissions based on their inclusion in the assigned user fields.
- A team can be defined so that users can only see records relevant to them (e.g., a user can see only data related to their team).
4. Field-Level Permissions
- Moving down the hierarchy, field permissions are inherited from the user group, but they can be customized.
Permissions on fields can include view only, edit and view, or team-based permissions.
5. Widget Permissions
- Widgets in the system are configurable to define which user groups can see them.
- The information displayed in the widget is filtered based on the permissions of the user accessing it. This ensures users only see data they are allowed to interact with.
6. Conditional Permissions
- Choice Boxes (single or multiple selections): Permissions can be defined based on the possible values in the choice fields.
- By doing so, permissions can be granted or restricted based on specific selected values in a field.
7. Data Export and Reports
- Any data shown to the user, including reports and exports, is governed by the user’s permissions.
- If a user does not have permission to view certain records, those records will not be displayed in reports or exports.
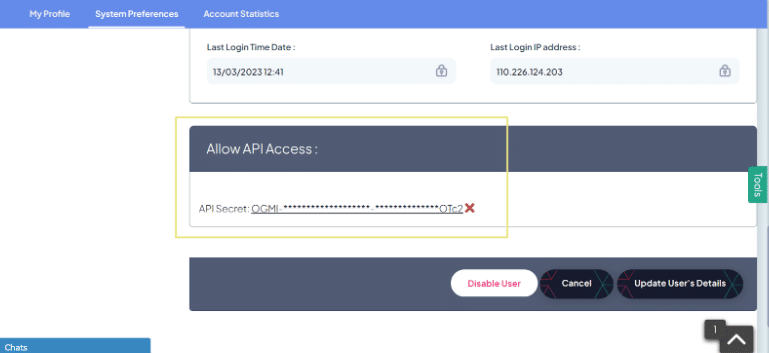
8. API Permissions
- For API access, the user must authenticate with a username and API SECRET KEY.
The API permissions are controlled based on the user’s permissions. A user must be an active user within the system for their permissions to apply to API requests.
This system ensures that permissions are granular and dynamic, allowing flexible control of who can do what within the system. By using user groups, team permissions, and field-level permissions, businesses can tightly control access to sensitive data, ensuring that the right people have the right level of access to perform their tasks.